Describe the Structure of the Spleen
The spleen is the largest lymphatic organ in the body. Key Points The structure of the spleen is such that two compartments can be distinguished.
Terms in this set 9 spleen.

. It is covered by a weak capsule that protects the organ whilst allowing it to expand in size. The spleen is a unique lymphoid organ that filters blood rather than lymph. Structure and Function of the Spleen.
The spleen is surrounded by a thin capsule covered by peritoneum mesothelial cells. The spleen is encased in a thick connective-tissue capsule. Here well discuss more about each of these important features.
Visceral surface in contact with the other abdominal viscera. The spleens primary functions are to filter the blood and help defend the body against pathogens. You may have heard people use the phrase venting spleen not referring to the body part itself but as a way to describe letting out anger or frustration.
The spleen is divided by function and structure into the red and white pulp. The word spleen has come to be used metaphorically as a synonym for anger. The spleen is very vascular and reddish purple in color.
Thus the spleen is situated between the fundus of the stomach and the diaphragm. The blood-containing red pulp. However the WP makes up less than a quarter of splenic tissue.
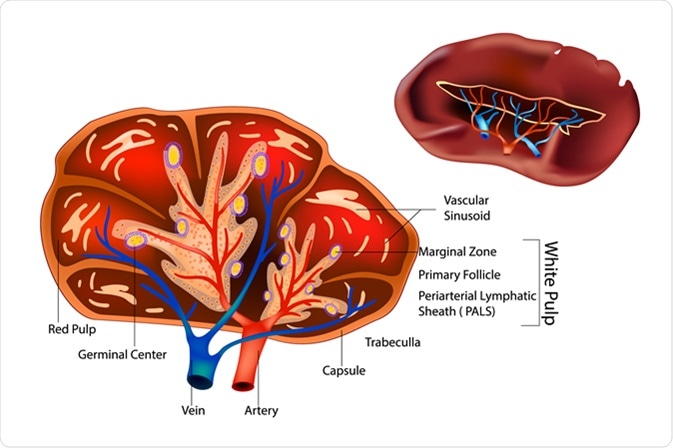
These functions are carried out by the 2 main compartments of the spleen the white pulp including the marginal zone and the red pulp which are vastly different. It is wrapped by a fibroelastic capsule which allows the. In between these two regions is the marginal zone MZ in rodents and the perifollicular zone in humans 1 2 Fig.
These tissues are encased within a membrane of tissue. The spleen is located in the upper left abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm and posterior to the stomach. The spleen is composed of two functionally and morphologically distinct compartments the white pulp and the red pulp.
This function in combination with a highly organized lymphoid compartment makes the spleen the most. The white pulp is lymphoid tissue that usually surrounds splenic blood vessels. Its size and weight vary.
The outer surface of the spleen can be anatomically divided into two. Immune surveillance erythropoiesis removal of aged and damaged red blood cells from the blood plasma protein production. The spleen varies in size and shape between people but its commonly fist-shaped purple and about.
The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ in the body. In this article we will explain its anatomy what it does and what happens when it goes wrong. The spleen has a slightly oval shape.
Histologically the spleen is formed of stroma and parenchyma. The spleen has diaphragmatic and. Being an intraperitoneal organ the spleen is covered by a layer of visceral.
It is similar to a lymph node in shape and structure but it is much larger. The spleen in dogs is able to expand to store large numbers of erythrocytes but it is also capable of rapid contraction. Structure of Spleen It is a dark purple-coloured organ which lies in the left hypochondriae region of the abdomen between the fundus of.
The structure of the spleen enables it to remove older erythrocytes from the circulation and leads to the efficient removal of blood-borne microorganisms and cellular debris. The spleen is the largest secondary immune organ in the body and is responsible for initiating immune reactions to blood-borne antigens and for filtering the blood of foreign material and old or damaged red blood cells. The spleens external surface can be divided into two portions.
In the red pulp pathogens and cellular debris as well as ageing erythrocytes are efficiently removed from the blood. The term should not be confused with the renal structure a Malpighian corpuscle renal corpuscle. Removes old RBCs holds reserve of blood recycles iron removes bacteria.
The diaphragmatic surface and the visceral surface. Its function is to filter the blood. The spleen is the largest organ of the lymphatic systemLocated in the upper left region of the abdominal cavity the spleens primary function is to filter blood of damaged cells cellular debris and pathogens such as bacteria and virusesLike the thymus the spleen houses and aids in the maturation of immune system cells called lymphocytes.
The spleen is an organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium and partly in the epigastrium. The white pulp WP is the primary immunologic region of the spleen in both species. This is because in medieval times the spleen was thought to be the literal physical source of a hot temper.
Diaphragmatic surface in contact with diaphragm and ribcage. It varies in size and weight during the lifetime of an individual but in an adult is usually about 12 cm long 8cm broad. Surrounded by a connective tissue capsule which extends inward to divide the organ into lobules the spleen consists of two types of.
In dogs for example the spleen is somewhat dumbbell shaped while in mice and rats its more uniform along the longitudinal axis. Following splenectomy surgical removal of the spleen in an adult which of the following splenic functions would be performed by the bone marrow or liver. Inside the mass of splenic tissue is of two types the red pulp and the white pulp which do not separate into regions but intermingle and are distributed throughout the spleen.
Organ near the stomach that produces stores and eliminates blood cells filters blood spleen function. 6 rows The spleen is a purple fist-sized organ. The spleen combines the innate and adaptive immune system in a uniquely organized way.
A spleen lymphoid region organized as lymphoid sheaths with both T-cell and B-cell compartments around the branching arterial vessels resembles lymph node structure. The white pulp is a highly organized lymphoid. The spleen consists of two different types of tissues red pulp and white pulp.
Histological structure of the spleen Stroma. The spleen is an organ in the upper far left part of the abdomen to the left of the stomach. There are a number of species differences in the gross and histologic appearance of the spleen.

Spleen Anatomy Definition Function And Location Biology

Structure Of The Spleen A The Spleen Parenchyma Is Protected By A Fi Download Scientific Diagram

Structure Of The Human Spleen Adapted From Bowdler 6 Arterial Blood Download Scientific Diagram

Spleen Structure And Functions

Spleen Anatomy And Physiology Youtube

Organization Of The Spleen The Spleen Is An Encapsulated Organ Which Download Scientific Diagram
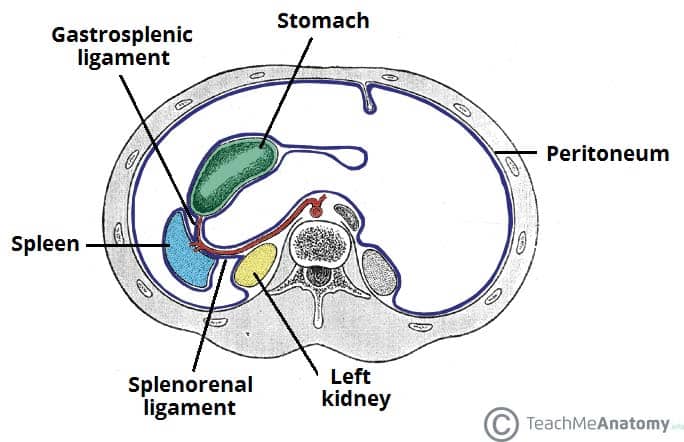
The Spleen Position Structure Neurovasculature Teachmeanatomy
Role Of The Spleen In Drug Metabolism

Anatomy Of The Spleen Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub Youtube

The Lymphatic System 2 Structure And Function Of The Lymphoid Organs Nursing Times
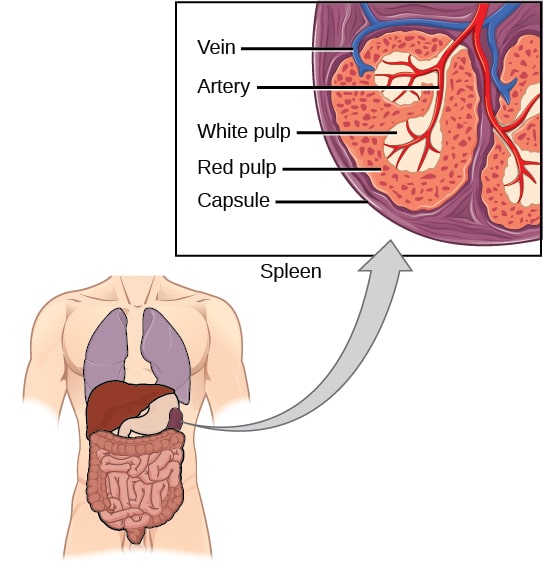
Function Of The Spleen Red Pulp White Pulp Teachmephysiology

Spleen Structure And Functions
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/504/GW9V4CDFeKGgg7oC9V7aQ_structure-of-spleen_english.jpg)
Spleen Anatomy Location And Functions Kenhub
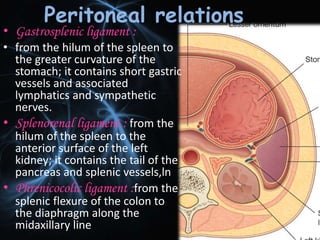
Structure And Function Of Spleen
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ligamentum-gastrosplenicum-2/71CjSePOD2DZqPh68mSfw_Lig._gastrosplenicum_01.png)
Spleen Anatomy Location And Functions Kenhub
Structure Of The Spleen Diagram Of Splenic Histology C Capsule Ca Download Scientific Diagram
Spleen Anatomy Histology Histology Flashcards Draw It To Know It
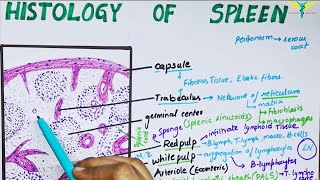

Comments
Post a Comment